If you understand the structure and function of bird skeletons, it would help you to get an insight into the evolution that happens over time and how they share a unique physiology. You would also get to understand the behavior of the bird and what changes or adaptations took place to help them survive in the present environment.
So, let’s get started.
Skeletal Anatomy of Birds Explained
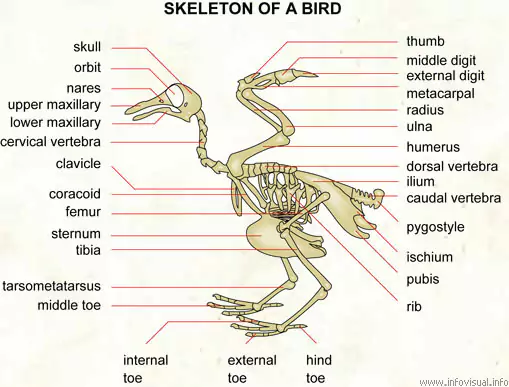
The skeletal system of the bird can be divided into two segments:
- Axial – The central axis of the body includes the skull, ribs, sternum, and vertebral column.
- Appendicular – It includes the pectoral and pelvic girdles, wings and legs
Axial
The skull consists of lower jaw bones, the roof of the mouth, bones of the tongue, the orbit of the eyes, and ridges of the beak. Ribs form a firm rib cage when the uncinate processes project from one rib to another. Sternum is flat in the case of flightless birds and board, flat, and narrow for the gallinaceous birds, attached to the flight muscles. The vertebral column is composed of a chain of bones including the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and caudal vertebrae
Appendicular
The pectoral girdle supports the wing bone and consists of three bones, coracoid bone, scapula, and furcula, making up the clavicle. Wings consist of humerus radius ulna carpal bone digits and carpometacarpus. The leg consists of the femur, patella, fibula, tibiotarsus, digits, metatarsal bone, and tarsometatarsus.
Unique Features of the Bird’s Skeletal System
- To provide them support during the flight, the vertebral section of the backbone of the bird gets fused together forming a rigid structure.
- When compared with other species, birds have comparatively smaller skulls which helps them to fly easily.
- To provide structural strength, the skeletal system of the bird has hollow bones.
- Instead of teeth, they have beaks that make them light in weight.
- To help them in their flight, the birds have a fused collarbone which is attached to the muscles.
How Does a Bird Skeleton Differ from Other Mammalian Skeletons?
Natural selection is the sole factor based on which animals go through physical and structural adaptation, which helps them to take full advantage of the environment and begins to support them in feeding and reproduction.
Birds became adapted to flight and based on that they went through skeletal changes, such as –
Ossification
The bones of birds are thin and lightweight but stiff, dense, and compact. The vertebrae went through fusion to form a rigid spinal column that supports flight.
Pneumatic Bone
Birds have hollow bones also known as pneumatic which help them to take flight for long distances. These are honeycomb-like structures with cross-sections. The medullary cavity of the pneumatic bones in birds consists of a diverticula of the internal air sac However, based on the distance traveled and breed of the bird, the intensity of pneumatic bones changes. In Gallinaceous birds, the pelvis, cervical, thoracic vertebrae, and sternum are pneumatic in nature.
Why is Studying Bird Bones Important?
Bird bones have pneumatic sacs that help to lighten the weight of the bird’s skeleton helping in flight and it also helps in respiration.
What is the Function of Bones in Birds?
The skeletal system of birds protects and supports the internal organs, such as the lungs and heart. It is the source of calcium during egg production. It also helps in walking and flight due to the articulated and jointed system. Bones also provide a supportive matrix for stem cells which form cells for hematopoiesis and granulopoiesis.
What is the Bone Composition in birds?
The bones in birds are made of inorganic and organic matrix, where the inorganic matrix has bone mineral content with 65% Bone ash and consists of hydroxyapatite. These inorganic components form a major part of bones and teeth and are responsible for hardness and strength. The organic matrix which consists of 35% of the bone consists of protein of Type 1 collagen and provides flexibility to the bone.
Which are Stronger Bones in Birds?
The shoulder bones are considered to be stronger in birds and they help them to take flight. The flight muscles are held by the breast bones which are used to move the wings up and down while they are flying. Also, the bones provide them with a streamlined body structure which helps to reduce air resistance while flying.


![Can Ducks Have Celery? [Explained] 8 Can Ducks Have Celery](https://masterbirds.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/can-ducks-have-celery-768x432.webp)

